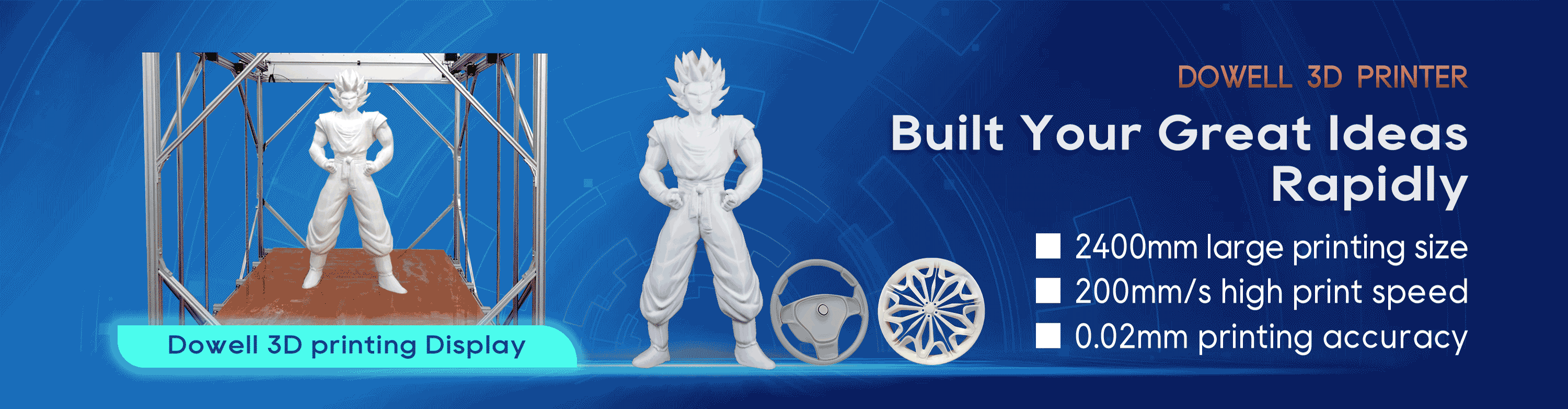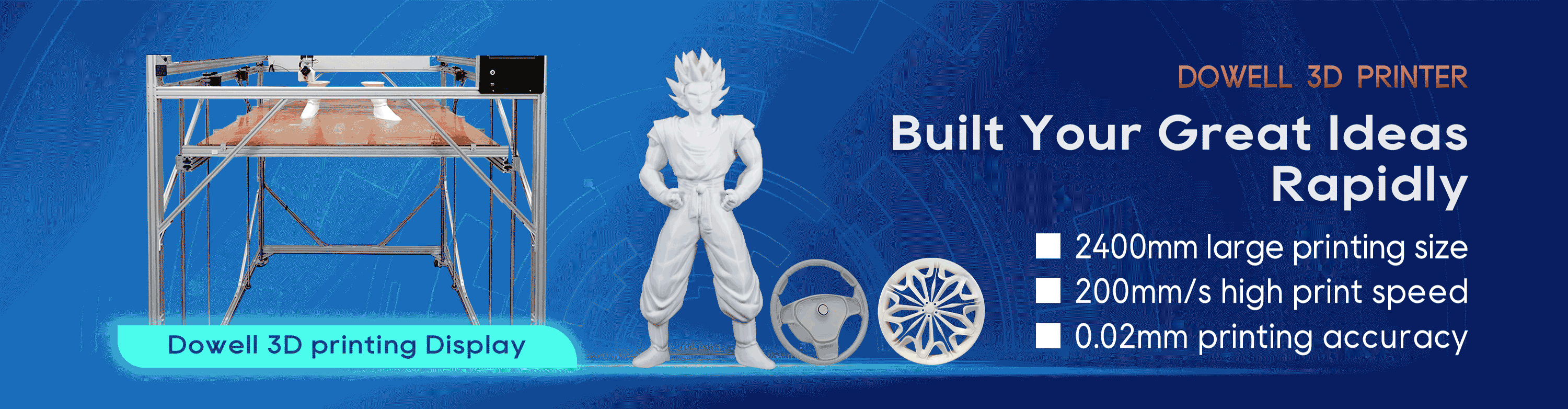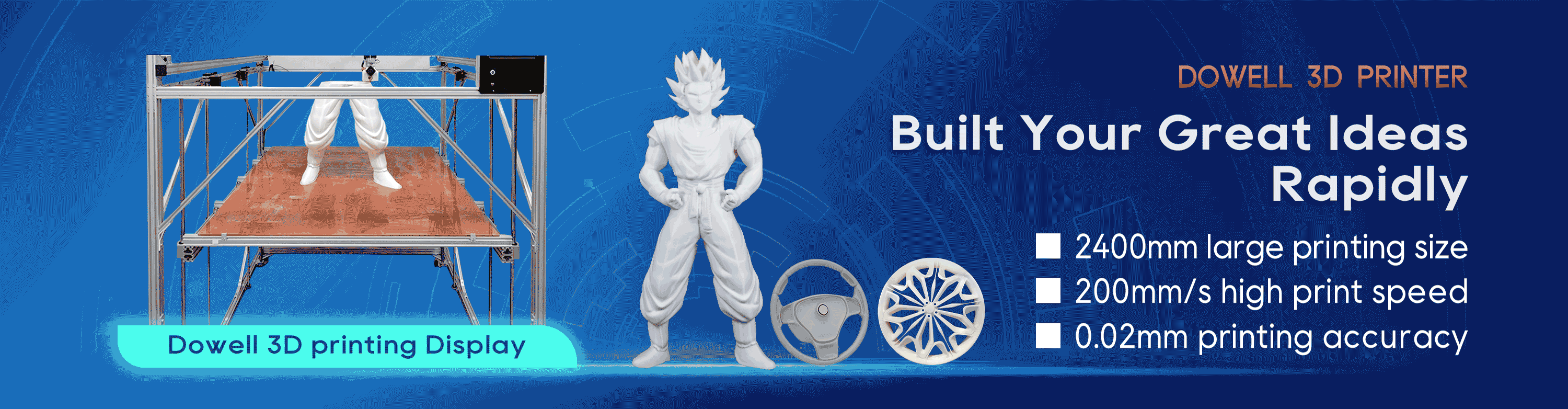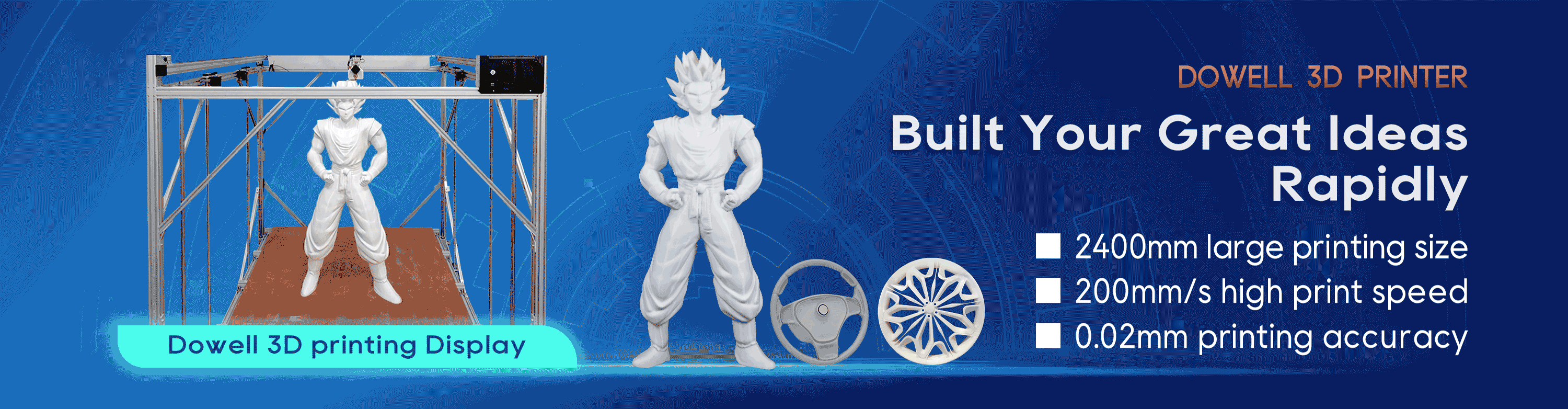
3D fdm printing and environmental protection
FDM 3d printing has two key attributes, and it is these two attributes that enthusiasts call "green" technology. First, many 3D printing systems produce little waste, which is different from traditional manufacturing techniques (such as injection molding, casting, stamping, and cutting). Second, 3D printers in homes, stores, and community centers can use digital designs to manufacture products on-site, reducing the need to ship products to end users.
However, quantitative analysis of the environmental performance of 3d plastic printer printing is limited. Most of it only focuses on the energy used in the production process, and does not include the impact of raw material production, the use of the product itself, or waste management. To fill this gap, we organized a special edition of Yale University's "Journal of Industrial Ecology". We found that the excitement about the possibility of drastically improving the environment needs to be alleviated by understanding how this technology is implemented and the current state of development.
Mainly used in industry
Most consumers who have seen 3D printing machines know that they are small, box-shaped machines similar to inkjet printers. These systems can make simple products such as door stops, bottle openers and shopping bag handles, and are usually made of a single material.
In fact, 3D printing is a series of technologies mainly used in industry, which is called laminated manufacturing. These systems generate objects based on digital information by adding continuous layers of material. These items are then further processed and assembled into products such as jet engine components, hearing aids, medical implants and many different types of complex parts used in industrial equipment. Therefore, laminated manufacturing is a supplement to traditional manufacturing processes, not a substitute for them.
For decades, the industry has used laminated manufacturing to create prototypes for product design and production planning. Now, these technologies are becoming more and more mature and are used to manufacture end-use parts and products.
Laminated manufacturing is particularly useful for producing customized parts and small batches of complex objects at a lower cost than traditional manufacturing, which usually requires time-consuming and expensive production equipment preparation.