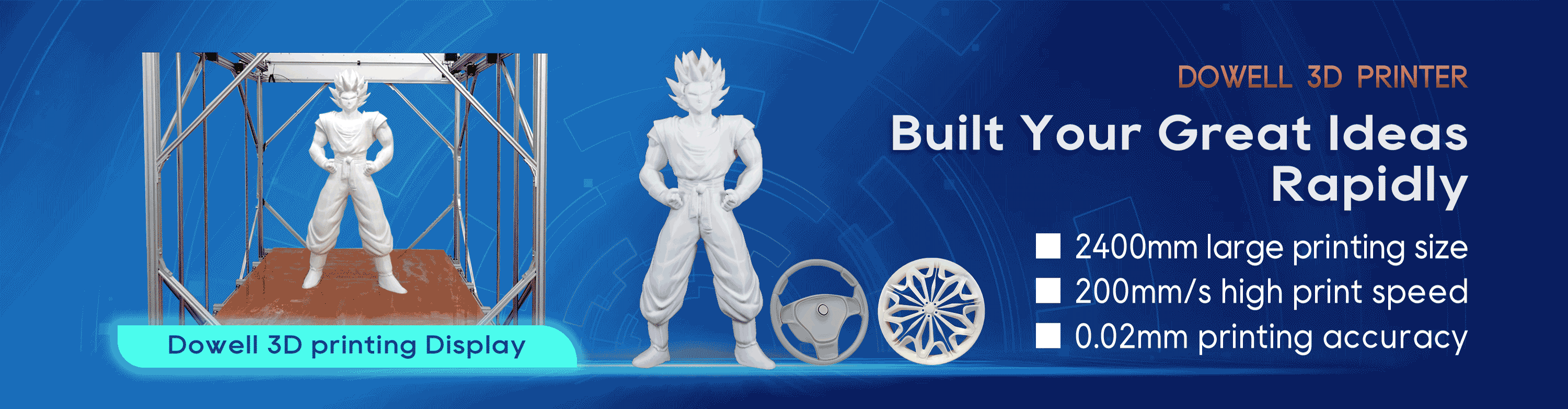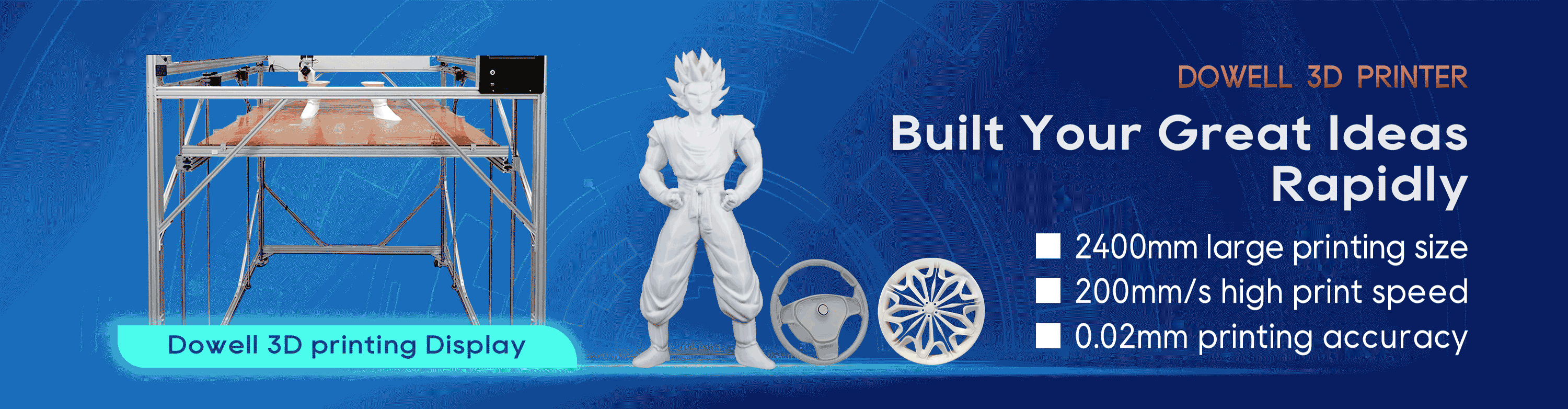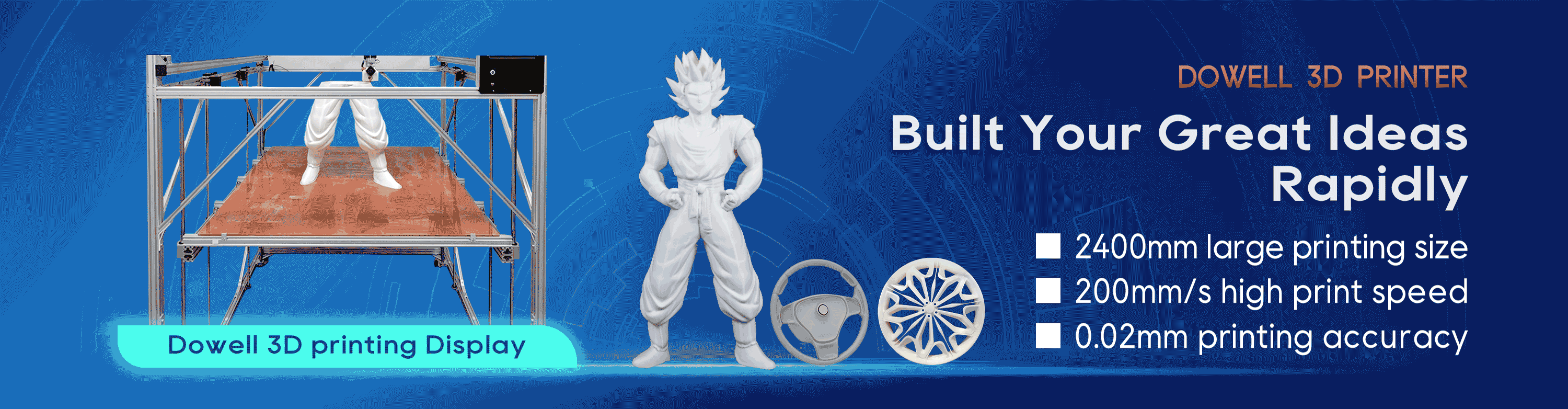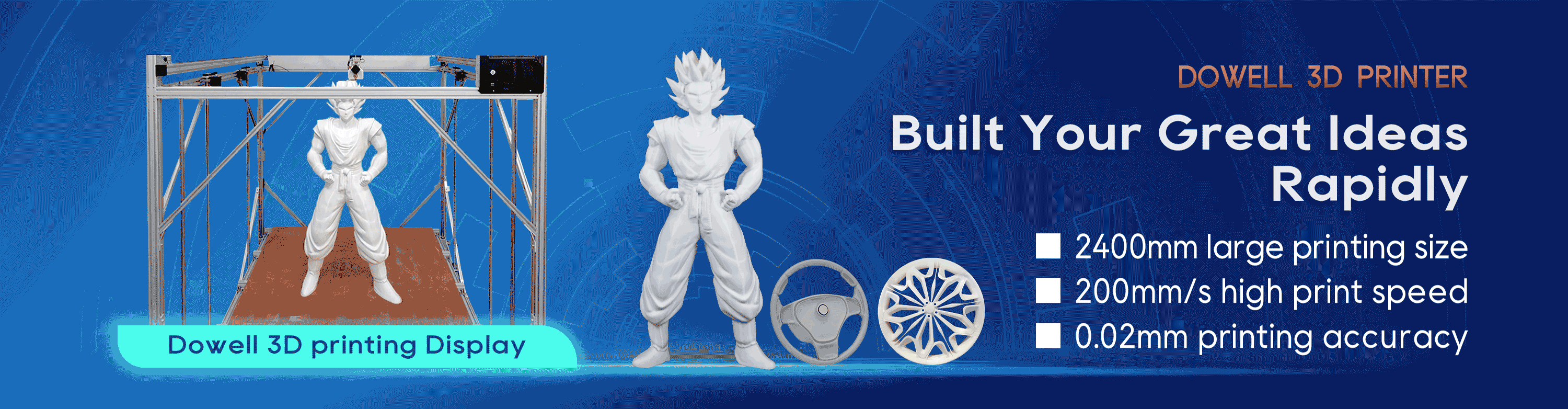
How Does 3D Printing Printer Work?
WHAT IS 3D PRINTING?
3D printing uses specialized equipment to create solid, three-dimensional objects from a digital file. The practice has been around since the 1980s, when Charles W. Hull invented the process and created the first 3D-printed part. Since then, the field of 3D printing has grown exponentially and holds countless possibilities.
3D Printing Overview
3D printing is a process that uses computer-aided design, or CAD, to create objects layer by layer. 3D printing is commonly used in manufacturing and automotive industries, where tools and parts are made using 3D printers.
As the capabilities of 3D printing continue to grow, so does its value: By 2029, the 3D printing industry is estimated to reach a value of $84 billion. This growth means we are bound to interact with products — and even homes and buildings — made with 3D printing.
3D printing is also shaking up the healthcare industry. In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic overwhelmed hospitals and increased the need for personal protective equipment. Many healthcare facilities turned to 3D printing to supply their staff with much-needed protective equipment, as well as the parts to fix their ventilators. Large corporations, startups and even high school students with 3D printers stepped up to the plate and answered the call. 3D printing will not only change how we make PPE and medical equipment, but also streamline prosthetics and implants.
Although 3D printing is not necessarily new, there are some who still wonder what 3D printing is and how it works. Here’s a guide to understanding 3D printing.
What Are 3D Printers?
In short, 3D printers use CAD to create 3D objects from a variety of materials, like molten plastic or powders. 3D printers can come in a variety of shapes and sizes ranging from equipment that can fit on a desk to large construction models used in the making of 3D-printed houses. There are three main types of 3D printers and each uses a slightly different method.
TYPES OF 3D PRINTERS
Stereolithographic, or SLA printers, are equipped with a laser that forms liquid resin into plastic.
Selective laser sintering, or SLS printers, have a laser that sinters particles of polymer powder into an already solid structure.
Fused deposition modeling, or FDM printers, are the most common. These printers release thermoplastic filaments that are melted through a hot nozzle to form an object layer by layer.
3D printers aren’t like those magical boxes in sci-fi shows. Rather, the printers — which act somewhat similarly to traditional 2D inkjet printers — use a layering method to create the desired object. They work from the ground up and pile on layer after layer until the object looks exactly like it was envisioned
Why Are 3D Printers Important to the Future?
The flexibility, accuracy and speed of 3D printers make them a promising tool for the future of manufacturing. Today, many 3D printers are used for what is called rapid prototyping.
Companies all over the world now employ 3D printers to create their prototypes in a matter of hours, instead of wasting months of time and potentially millions of dollars in research and development. In fact, some businesses claim that 3D printers make the prototyping process 10 times faster and five times cheaper than the normal R&D processes.
3D printers can fill a role in virtually almost every industry. They’re not just being used for prototyping. Many 3D printers are being tasked with printing finished products. The construction industry is actually using this futuristic printing method to print complete homes. Schools all over the world are using 3D printers to bring hands-on learning to the classroom by printing off three-dimensional dinosaur bones and robotics pieces. The flexibility and adaptability of 3D printing technology makes it a game-changer for any industry.
What Can You 3D Print?
3D printers have extreme flexibility for what can be printed with them. For instance, they can use plastics to print rigid materials, like sunglasses. They can also create flexible objects, including phone cases or bike handles, using a hybrid rubber and plastic powder. Some 3D printers even have the ability to print with carbon fiber and metallic powders for extremely strong industrial products. Here are a few of the common applications 3D printing is used for.
Rapid Prototyping and Rapid Manufacturing
3D printing provides companies with a low-risk, low-cost and fast method of producing prototypes that allow them to test a new product’s efficiency and ramp up development without the need for expensive models or proprietary tools. Taken a step further, companies across many industries utilize 3D printing for rapid manufacturing, allowing them to save costs when producing small batches or short the printing time.
Functional Parts
3D printing has become more functional and precise over time, making it possible for proprietary or inaccessible parts to be created and acquired so a product can be produced on schedule. Additionally, machines and devices wear down over time and may be in need of swift repair, which 3D printing produces a streamlined solution to.
Tools
Like functional parts, tools also wear down over time and may become inaccessible, obsolete or expensive to replace. 3D printing allows tools to be easily produced and replaced for multiple applications with high durability and reusability.
Models
While 3D printing may not be able to replace all forms of manufacturing, it does present an inexpensive solution to producing models for visualizing concepts in 3D. From consumer product visualizations to architectural models, medical models and educational tools. As 3D printing costs fall and continue to become more accessible, 3D printing is opening new doors for modeling applications.