3-Guide to 3D Printing: Materials, Types, Applications, and Properties
SLS 3D Printing
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing is trusted by engineers and manufacturers across a variety of industries for its ability to produce strong, functional parts. Low cost, high production rates, and mature materials make the technology ideal for a range of applications from rapid prototyping to manufacturing assistance and low-volume, bridge, or custom manufacturing.
Because the unfused powder supports the part during printing, no specialized support structures are required. This makes SLS ideal for complex geometries, including internal features, undercuts, thin walls, and negative features.
Like SLA, SLS 3D prints are generally isotropic. The surface finish of SLS parts is slightly rough due to the powder particles, but there are few visible layer lines, and SLS 3D prints can be easily post-processed to further improve mechanical properties and appearance.
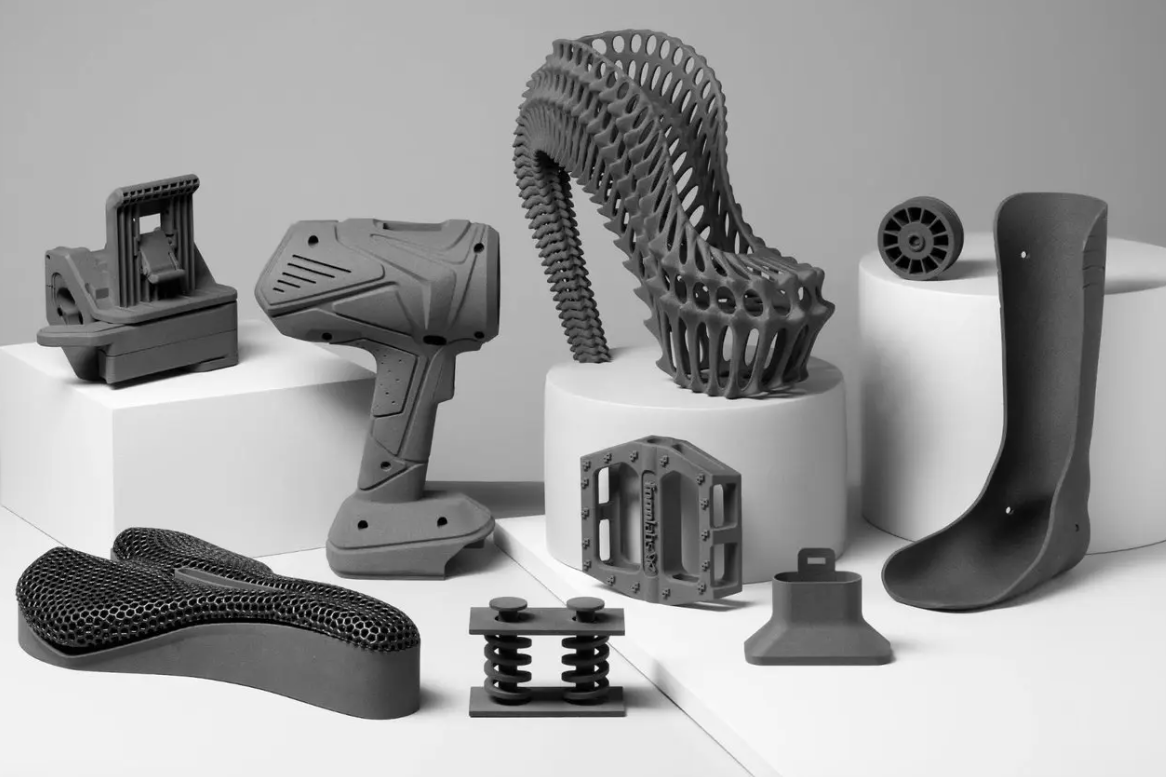

SLS 3D printing materials are ideal for a range of functional applications, from engineering consumer products to manufacturing and healthcare.
Popular SLS 3D Printing Materials
The material selection for SLS is limited compared to FDM and SLA, but the available materials have excellent mechanical characteristics, with strength resembling injection-molded parts. The most common material for selective laser sintering is nylon, a popular engineering thermoplastic with excellent mechanical properties. Nylon is lightweight, strong, and flexible, as well as stable against impact, chemicals, heat, UV light, water, and dirt. Other popular SLS 3D printing materials include polypropylene (PP) and the flexible TPU.
MATERIAL | DESCRIPTION | APPLICATIONS |
Nylon 12 | Strong, stiff, sturdy, and durable | Functional prototyping |
Nylon 11 | Similar properties to Nylon 12, but with a higher elasticity, elongation at break, and impact resistance, but lower stiffness | Functional prototyping |
Nylon composites | Nylon materials reinforced with glass, aluminum, or carbon fiber for added strength and rigidity | Functional prototyping |
Polypropylene | Ductile and durable | Functional prototyping |
TPU | Flexible, elastic, and rubbery | Functional prototyping |
Compare Plastic 3D Printing Materials and Processes
Different 3D printing materials and plastic 3D printing processes have their own strengths and weaknesses that define their suitability for different applications. The following table provides a high level summary of some key characteristics and considerations.
| FDM | SLA | SLS |
Pros | Low-cost consumer machines and materials available | Great value | Strong functional parts |
Cons | Low accuracy | Sensitive to long exposure to UV light | More expensive hardware |
Applications | Low-cost rapid prototyping | Functional prototyping | Functional prototyping |
Materials | Standard thermoplastics, such as ABS, PLA, and their various blends on consumer level machines. High performance composites on high cost industrial machines | Varieties of resin (thermosetting plastics). Standard, engineering (ABS-like, PP-like, flexible, heat-resistant), castable, dental, and medical (biocompatible). Pure silicone and ceramic. | Engineering thermoplastics. Nylon 11, nylon 12, glass or carbon-filled nylon composites, polypropylene, TPU (elastomer). |